In this tutorial, we’ll explore how to trigger GitHub Actions workflows from Azure Logic Apps without relying on Personal Access Tokens (PATs). Instead, we’ll utilize GitHub App authentication, which offers enhanced security and scalability for automated workflows.
🧩 Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure you have the following:
- An Azure Logic App (Standard).
- A GitHub App installed in your GitHub organization or personal account.
- Access to Azure Key Vault to securely store your GitHub App’s private key.
🔑 GitHub App
- Navigate to your GitHub account settings.
- Under Developer settings, select GitHub Apps.
- Click New GitHub App and fill in the required details:
- Name: Choose a descriptive name for your app.
- Homepage URL: Provide a URL for your app’s homepage.
- Webhook URL: Optional, specify a webhook URL if needed.
- Webhook secret: Optional, set a secret for webhook validation.
- Under Permissions & events, grant the necessary permissions for your app. For triggering workflows, ensure the app has the appropriate repository permissions.
- Scroll down to the Private keys section and click Generate a private key.
- Download the
.pemfile; this will be used for authentication.
🗝️ Private Key in Azure Key Vault
- Open the Azure portal and navigate to your Key Vault.
- Under Secrets, click + Generate/Import.
- Name the secret (e.g.,
GitHubAppPrivateKey) and upload the Base64 encoded contents of your.pemfile. You can generate the Base64 for the PEM file using this commandbase64 myPEM.private-key.pem > base64.key - Ensure the secret is set to Enabled.
⚙️ Azure Logic App to Retrieve the Secret
- In your Logic App designer, add a new action: Get secret.
- Configure the action to connect to your Key Vault and retrieve the
GitHubAppPrivateKeysecret. - Ensure that the action is properly authenticated and has the necessary permissions to access the Key Vault.
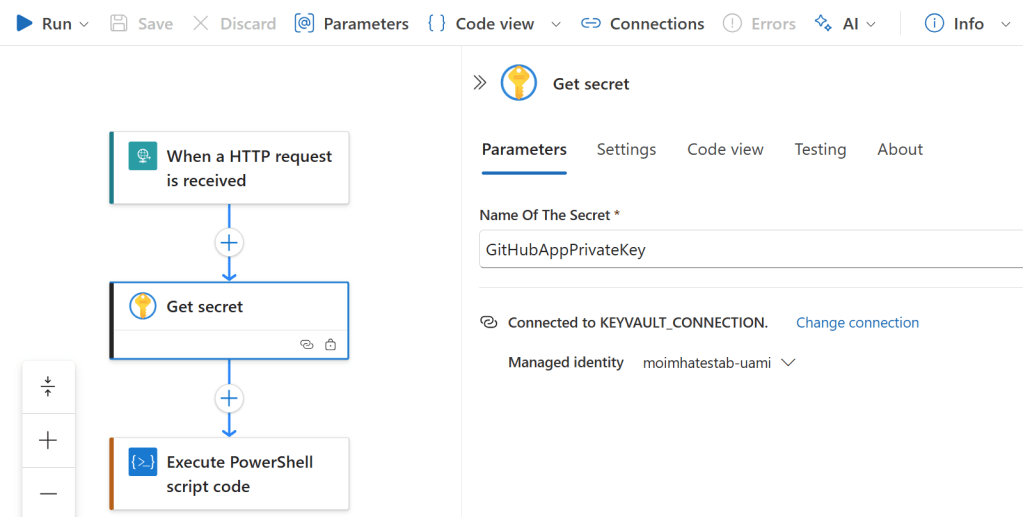
🧪 PowerShell Script to Trigger Workflow
Add an Inline Code action with the following PowerShell script:
# 1. Retrieve the secret as JToken
$kvOutput = Get-ActionOutput -ActionName 'Get_secret'
$privateKeyValue = $kvOutput.outputs.body.value
# 2. Force it into a guaranteed string
$privateKeyBase64 = $privateKeyValue.ToString()
if ([string]::IsNullOrEmpty($privateKeyBase64)) {
Throw "Secret 'GitHubAppPrivateKey' is empty or missing."
}
# 3. Embedded constants
$appId = '334444444'
$installationId = '555555555'
$repoOwner = 'YOUR REPO OWNER NAME'
$repoName = 'YOUR REPO NAME'
$workflowFile = 'main.yml'
$ref = 'main'
# 4. Decode PEM
$pem = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String($privateKeyBase64))
# JWT Header
$header = @{ alg="RS256"; typ="JWT" } | ConvertTo-Json -Compress
$headerEncoded = [Convert]::ToBase64String([Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes($header)).TrimEnd('=') -replace '\+','-' -replace '/','_'
# JWT Payload
$payload = @{
iat = [DateTimeOffset]::UtcNow.AddSeconds(-60).ToUnixTimeSeconds()
exp = [DateTimeOffset]::UtcNow.AddMinutes(10).ToUnixTimeSeconds()
iss = $appId
} | ConvertTo-Json -Compress
$payloadEncoded = [Convert]::ToBase64String([Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes($payload)).TrimEnd('=') -replace '\+','-' -replace '/','_'
# Sign JWT
$rsa = [System.Security.Cryptography.RSA]::Create()
$rsa.ImportFromPem($pem)
$dataToSign = "$headerEncoded.$payloadEncoded"
$sigBytes = $rsa.SignData(
[System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes($dataToSign),
[System.Security.Cryptography.HashAlgorithmName]::SHA256,
[System.Security.Cryptography.RSASignaturePadding]::Pkcs1
)
$signature = [Convert]::ToBase64String($sigBytes).TrimEnd('=') -replace '\+','-' -replace '/','_'
$jwt = "$dataToSign.$signature"
# Get the installation access token
$installUrl = "https://api.github.com/app/installations/$installationId/access_tokens"
$installRes = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Uri $installUrl -Headers @{
Authorization = "Bearer $jwt"
Accept = "application/vnd.github+json"
"User-Agent" = "LogicApp-Pwsh"
}
$installationToken = $installRes.token
if (-not $installationToken) { Throw "Installation token retrieval failed." }
# Dispatch the workflow
$dispatchUrl = "https://api.github.com/repos/$repoOwner/$repoName/actions/workflows/$workflowFile/dispatches"
Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Uri $dispatchUrl -Headers @{
Authorization = "Bearer $installationToken"
Accept = "application/vnd.github+json"
"User-Agent" = "LogicApp-Pwsh"
} -Body (@{ ref = $ref } | ConvertTo-Json)
# Return success
Push-WorkflowOutput -Output ([PSCustomObject]@{ Result = "Workflow dispatched successfully." })
Replace placeholders like <Your GitHub App ID>, <Your Installation ID>, <Owner>, <Repository>, and <Workflow File> with your actual values.
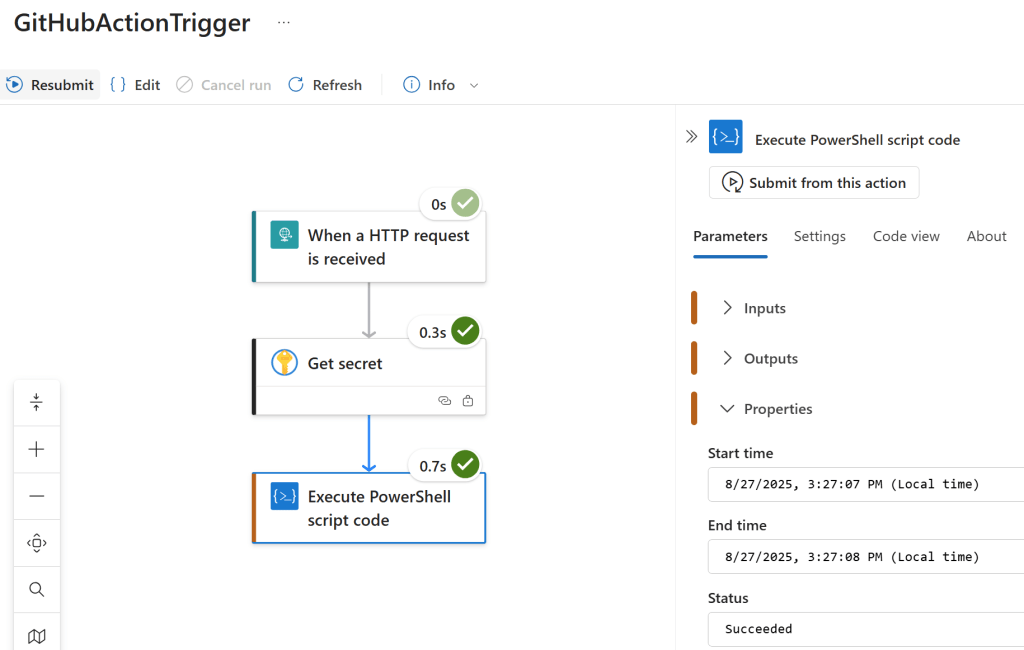
✅ Test the Workflow
- Save and run your Logic App.
- Monitor the run history to ensure the workflow is triggered successfully.
- Check your GitHub repository’s Actions tab to confirm that the workflow has been initiated.
🧪 C# code to Trigger Workflow
In case, you prefer C# as oppose to PowerShell the following C# code can deliver the same result:
First, install these NuGet packages:
dotnet add package System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt
dotnet add package Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens
dotnet add package System.Net.Http.Json
C# code to trigger the workflow using GitHub API:
public class GitHubAppDispatcher
{
private const int AppId = YOUR_APP_ID; // e.g. 1851818
private const long InstallationId = YOUR_INSTALLATION_ID; // e.g. 83026199
private const string RepoOwner = "MoimHossain";
private const string RepoName = "your-repo";
private const string WorkflowFile = "main.yml";
private const string Branch = "main";
public static async Task Main()
{
// 1. Load private key (plaintext PEM) from secure store (e.g., Key Vault)
string privateKeyPem = await LoadPrivateKeyAsync();
// 2. Generate JWT
var jwt = GenerateJwt(privateKeyPem);
// 3. Exchange for installation token
var installToken = await GetInstallationTokenAsync(jwt);
// 4. Dispatch GitHub Actions workflow
await TriggerWorkflowAsync(installToken);
Console.WriteLine("Workflow dispatch triggered successfully.");
}
private static string GenerateJwt(string privateKey)
{
using var rsa = RSA.Create();
rsa.ImportFromPem(privateKey.ToCharArray());
var credentials = new SigningCredentials(new RsaSecurityKey(rsa),
SecurityAlgorithms.RsaSha256);
var now = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow;
var token = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: AppId.ToString(),
audience: null,
notBefore: now.UtcDateTime.AddSeconds(-60),
expires: now.UtcDateTime.AddMinutes(10),
signingCredentials: credentials
);
return new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(token);
}
private static async Task<string> LoadPrivateKeyAsync()
{
// Placeholder: Retrieve your base64-encoded **PEM** from Key Vault or config
// For example, use Azure.Identity and Azure.Security.KeyVault.Secrets packages here
}
}
To retrive the installation token from the PEM:
private static async Task<string> GetInstallationTokenAsync(string jwt)
{
using var http = new HttpClient();
http.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Bearer", jwt);
http.DefaultRequestHeaders.UserAgent.Add(new ProductInfoHeaderValue("GHApp", "1.0"));
var url = $"https://api.github.com/app/installations/{InstallationId}/access_tokens";
var response = await http.PostAsync(url, null);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
using var doc = await JsonDocument.ParseAsync(await response.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync());
return doc.RootElement.GetProperty("token").GetString();
}
Triggering the workflow with the token:
private static async Task TriggerWorkflowAsync(string token)
{
using var http = new HttpClient();
http.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Bearer", token);
http.DefaultRequestHeaders.UserAgent.Add(new ProductInfoHeaderValue("GHApp", "1.0"));
var url = $"https://api.github.com/repos/{RepoOwner}/{RepoName}/actions/workflows/{WorkflowFile}/dispatches";
var body = JsonSerializer.Serialize(new { ref = Branch });
var response = await http.PostAsync(url, new StringContent(body, System.Text.Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"));
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
🔐 Security Considerations
- Secure Inputs and Outputs: In the Logic App designer, ensure that sensitive data is marked as secure to prevent exposure in run history.
- Limit Permissions: Grant the GitHub App only the necessary permissions to minimize security risks.
- Rotate Keys Regularly: Periodically regenerate and update the private key stored in Azure Key Vault.
🧠 Conclusion
By leveraging GitHub App authentication, you can securely trigger GitHub Actions workflows from Azure Logic Apps without relying on PATs. This approach enhances security and scalability for your automated workflows.